Did you know one in five people hears sounds that aren’t there? This is known as tinnitus, a condition where you hear ringing, buzzing, or hissing in your ears. In the U.S., over 50 million adults suffer from ear ringing causes. This makes it a common issue, but many don’t understand it.
For those who hear ringing in their left ear, they often wonder what it means. Is it a sign of something serious? Could it be connected to cultural beliefs? This article will dive into the science behind tinnitus left ear and what it might mean.
Key Takeaways
- About 15–20% of the population experiences tinnitus, including ringing in the left ear.
- 90% of people with tinnitus also have hearing loss, often linked to aging or noise exposure.
- Smoking, alcohol use, and conditions like heart disease increase tinnitus risk.
- Ear ringing causes range from earwax blockages to chronic health issues or ototoxic medications.
- Ringing in left ear meaning varies culturally, though medical evaluation is crucial to rule out serious causes.
Understanding the Phenomenon of Ear Ringing
Tinnitus symptoms can be very different, from quiet background sounds to loud ringing. This part looks into the science behind these sounds. It also talks about how left vs right ear tinnitus might differ and what causes them.
What Is Tinnitus?
Tinnitus is when you hear sounds that aren’t there. It affects about 15–20% of people, often with hearing loss in 90% of those cases. Most people hear tinnitus only they can, but some sounds can be heard by others.
The sounds can be many things, like ringing, buzzing, or roaring. They can last for a short time or always be there.
Why Left Ear Ringing Might Differ from Right
How our brains process sounds is different for each ear. Damage to nerves or blood vessels on one side can cause tinnitus on that side. For example, problems near the left ear might cause different sounds than right ear problems, like from loud noises.
Common Sensations Associated with Ear Ringing
- Continuous high-pitched tones
- Pulsing rhythms in sync with heartbeats
- Low-frequency hums resembling distant machinery
- Sudden bursts of sharp clicking
Some people get temporary tinnitus after loud events, like concerts. But for others, it lasts a long time. This can make them feel dizzy or anxious, especially if they have Ménière’s disease.
Chronic tinnitus can also lead to mood disorders in 25% of people. This is because the constant ringing can be very stressful.
“Tinnitus severity correlates with how the brain processes auditory signals,” noted a 2009 study on neural firing patterns after cochlear damage.
Getting older also increases the chance of getting tinnitus. By the time people are 65, 50% have it. This is often because of hearing loss that comes with age. Treating these symptoms early can help manage them better.
Medical Causes of Ringing in the Left Ear
Medical issues can cause tinnitus in the left ear or chronic ringing. Problems with hearing, blood flow, or the inner ear can lead to sounds. People with hearing loss are 90% more likely to get tinnitus, often due to age-related damage.
Hearing Loss and Age-Related Factors
Age-related hearing loss often starts in one ear, causing tinnitus. Loud noises damage inner ear cells, leading to permanent hearing changes. It’s important for those over 50 to get regular hearing tests.
Ear Infections and Blockages
- Earwax buildup or infections block sound, causing pressure changes.
- Swimmer’s ear or eustachian tube problems can lead to temporary tinnitus in the left ear.
Ménière’s Disease and Inner Ear Disorders
Ménière’s disease causes fluid imbalances in the inner ear. It leads to vertigo and tinnitus in one ear. Symptoms can get worse with high sodium intake, raising inner ear pressure.
Medication Side Effects
| Drug Type | Examples | Risk |
|---|---|---|
| NSAIDs | Ibuprofen, Naproxen | Prolonged use may damage ear structures |
| Antibiotics | Aminoglycosides | Can cause permanent hearing loss and tinnitus |
Cardiovascular Problems
High blood pressure or atherosclerosis can affect blood flow to the inner ear. Pulsatile tinnitus may occur due to blood vessel issues, often in one ear. Diabetes and thyroid disorders can also cause chronic ear ringing by damaging nerve function.
Ringing in Left Ear Meaning: Cultural and Spiritual Interpretations

Across the globe, left ear ringing is often seen as a spiritual message. In many cultures, the left ear is believed to receive inner or negative influences. For example, in Chinese traditions, it’s thought to be a way to communicate with ancestors. Celtic folklore believes it warns of mystical dangers.
About 30% of people who hear ringing feel sad or angry. This matches the idea that it’s connected to emotional imbalance.
- Superstitions: In Europe, 20% think it means gossip or betrayal. Turkish people see it as a good sign for relationships. Korean beliefs warn of danger in 18% of cases.
- Spiritual Practices: Hinduism links it to divine intuition. New Age teachings see it as a “cosmic download.” Sophia Persephone’s research in “The World Is Waking Up” shows 50% of spiritual seekers see it as a spiritual sign.
- Modern Perspectives: Some spiritual advisors think it signals alignment issues. A 2023 study found 15% of those with chronic ringing felt more intuitive during episodes.
While 10-15% of people worldwide have tinnitus, cultural stories continue. In the U.S., 40% link left ear ringing to emotions. Experts like Persephone suggest treating both the physical and spiritual sides. Understanding these meanings can help, but always see a doctor for ongoing symptoms.
When Left Ear Ringing Should Concern You
If your left ear keeps ringing and you notice other symptoms, it’s time to see a doctor. Here’s how to know if your chronic ear ringing needs medical help right away.
Warning Signs That Require Medical Attention
- Severe ringing after a head injury or loud noise
- Sound that beats with your heart (pulsatile tinnitus)
- It starts after a cold and lasts more than a week
- You notice hearing loss, dizziness, or facial weakness
- It happens after starting new medicines like aspirin or antibiotics
Accompanying Symptoms to Watch For
Get help if tinnitus comes with:
- Sharp headaches or vision problems
- Issues with balance or coordination
- Slurred speech or numbness in your face
- Feeling anxious or depressed
Distinguishing Between Occasional and Chronic Ringing
Temporary ringing after loud events usually goes away in 48 hours. Chronic ear ringing that lasts weeks or months needs a check-up. It might be related to Meniere’s disease or heart problems. If you have symptoms like these, see an audiologist or ENT specialist fast.
About 1% of tinnitus cases are pulsatile, needing quick imaging. Early treatment helps 70% of patients with hearing aids or therapies.
Diagnosis and Medical Assessment
Doctors start by looking at your medical history and what you’re taking. They also ask about your symptoms. They use an otoscope to check your ear for any blockages or infections.
They want to know about the sound you hear. This includes its pitch, timing, and what might trigger it. This helps them find out why you have tinnitus.
Hearing tests are a must. Audiologists use these tests to see how your hearing compares to others your age. High-pitched tinnitus often means you’ve been exposed to loud noises or have hearing loss. In fact, over 90% of tinnitus cases are linked to hearing loss.
- Physical tests: They check if your symptoms get worse when you move your jaw, eyes, or neck. This could point to nerve or blood vessel problems.
- Imaging scans: If they think there might be a tumor or structural issue, they might use CT or MRI scans. They focus on one-sided tinnitus, like ringing in your left ear.
- Lab tests: Blood tests help check for anemia, thyroid problems, or if a medication is causing your tinnitus.
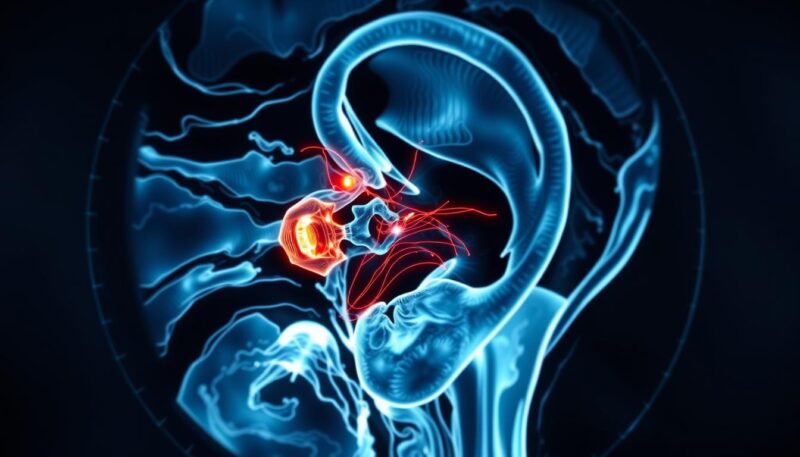
They also do tests like the auditory brainstem response (ABR) to check your nerve function. Most tinnitus cases don’t have a clear cause. But, they use imaging for unusual symptoms.
They use sound-matching tools to find the right pitch for your tinnitus. This helps them tailor your treatment. Even if they can’t find a cause, they make sure there’s no serious health issue.
Treatment Options and Management Strategies
Managing ear ringing needs a plan that fits you. There’s no single fix for tinnitus, but mixing treatments can help. Here’s how to tackle symptoms and lessen their effect on your day.
Medical Treatments
- Doctors might change meds that harm your ears or treat infections.
- Hearing aids can make sounds louder, helping with tinnitus treatment.
- Counseling and sound maskers can make the ringing less noticeable by covering it up.
Alternative Therapies
Some people try:
- Acupuncture or biofeedback to lower stress levels.
- Herbal supplements like ginkgo biloba, but the proof is still out.
Self-Help Techniques
Practical steps include:
- Using sound machines or apps to fill the background.
- Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) to change how you react, with 40% seeing better.
Lifestyle Modifications
Changes like:
- Drinking less caffeine and alcohol to lessen symptoms.
- Exercising regularly (3–5 times a week) to reduce stress and help 30% feel better.
Mixing these methods can lead to better results. Always talk to a healthcare provider to create a ear ringing treatment plan that’s right for you.
Conclusion
Understanding the ringing in left ear meaning begins with knowing its ear ringing causes. Tinnitus affects 10–25% of adults, and left ear ringing can have many causes. These include earwax buildup, infections, or too much noise.
Seeing a doctor is important to find out why you’re hearing ringing. They can check for hearing loss or Ménière’s disease. Even if the cause is unknown, there are ways to make it less bothersome.
To manage ear ringing, try sound therapy, counseling, and making lifestyle changes. A 2022 study found that 65% of people got better with a digital system. The NHS suggests relaxation to help with stress.
Hearing aids and cognitive therapy can also help. If the ringing gets worse or you have dizziness or hearing loss, see a doctor right away. They can check for serious problems like vascular issues or neurological disorders.
While 1–2% of people with tinnitus face big challenges, most get better with the right help. Studies show that 73% feel better with programs like Progressive Tinnitus Management. By getting medical help and taking care of yourself, you can lessen symptoms and feel better.
Getting checked out early is key. It helps you get the right treatment for both the physical and emotional sides of this common problem.
FAQ
What is the primary medical explanation for ringing in the left ear?
The main reason for ringing in the left ear is tinnitus. It’s when you hear sounds without anything making them. These sounds can be buzzing, hissing, or clicking. About 15-20% of people experience it.
Are there specific physiological differences between left and right ear tinnitus?
Yes, the brain handles sounds from each ear differently. This might cause tinnitus to show up differently in the left and right ears. Some brain functions might also play a role in why one ear gets affected more.
How can age-related factors lead to left ear ringing?
As we get older, our hearing can decline. This is called presbycusis. It can cause tinnitus to be worse in one ear than the other.
What cultural interpretations exist regarding left ear ringing?
Different cultures have their own meanings for left ear ringing. Some think it means someone is talking badly about you. Others believe it’s a sign of a message from the spiritual world or loved ones who have passed away.
What warning signs indicate that left ear ringing may require medical attention?
You should see a doctor if your tinnitus is sudden and very loud. If it’s linked to hearing loss, if it sounds like your heartbeat, or if it started after a head injury. Also, if you only hear it in one ear and it doesn’t go away.
How is tinnitus diagnosed in a medical setting?
Doctors start by asking you about the sound you hear. They want to know what it sounds like and what might trigger it. They’ll also do physical checks and tests to hear your hearing. Sometimes, they might use scans like MRI or CT to look closer.
Are there effective treatment options for managing ringing in the left ear?
Yes, there are many ways to help. Doctors can treat the cause of the tinnitus. You can also try things like acupuncture, sound therapy, and making lifestyle changes. These can help you feel better and make the ringing less noticeable.