Do you have frequent or occasional painful sensations along the urethra during or even after passing out urine? What could be causing this problem? Is it cancer, STDs, infection, diabetes or another external skin condition? Is it preventable? Find out more.
Pain or burning sensations can be felt when you just before passing out urine, every time you urinate or (occasionally) once in a while. Some people may feel the painful sensations around the pelvic region when they want to or while urinating.
Who gets this problem?
This largely depends on risks but anyone (males and females, young people and grownups) can face this problem. You have too many times keep an eye to know if your child is potentially having the same problem.
Causes, risks, and reasons
Read on to know what causes a burning or painful urination or when you are relieving yourself.
Acute prostatitis or chronic prostatitis

According to the The National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, prostatitis is a condition that causes frequent pains due to inflammation of the prostate. It can also involve the areas around it.
Up to then, there are four types which are chronic prostatitis, acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis and asymptomatic inflammatory prostatitis.
While some of the causes of chronic prostatitis may not be clear, acute bacterial prostatitis is caused by bacteria (which can migrate from the urethra to the prostate). The infection can occur suddenly but does not last for long.
We are not looking at everything but are more concerned with acute prostatitis.
Symptoms of acute bacterial prostatitis
- Burning sensation which is also felt as painful urination
- Urinating frequently and urge
- Fever and chills
- Nausea and vomiting
- Retaining urine in the bladder
- A problem to start peeing due to weakness in the system
This type of prostatitis can also be a signal that you have a urinary blockage or a UTI.
Chronic bacterial prostatitis
In addition to the frequency of urination, chronic prostatitis can also be signaled by burning urination accompanied by pain. Other symptoms include a painful ejaculation and feeling pain in the genital area.
Both acute and chronic bacterial prostatitis often cause a burning urination sensation.
NOTE: If you have a painful ejaculation (men) you should both seek medical attention promptly.
Urinary catheter infection
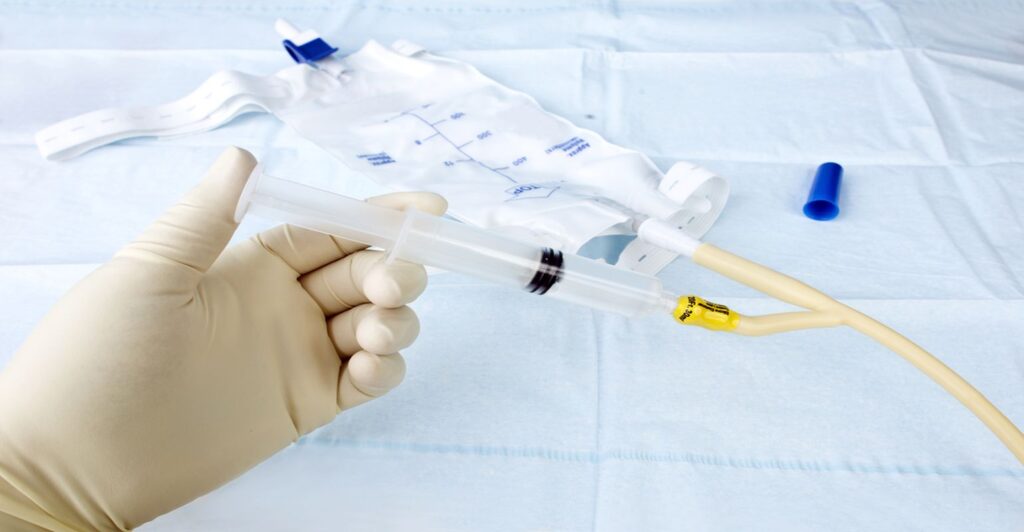
A urinary catheter is an external thin tube fixed into your body to help you drain urine under certain health problem or conditions. These include post-prostate cancer surgery, prostate enlargement or narrowing of the urethra.
Sometimes, the urinary catheter may become infected either by the infection causing germs moving from the urethra itself of if bacteria invade your body.
An infection will not only lead to burning sensation or painful feeling during peeing but also the kind of foods you will eat while using a catheter to urinate will add up to the effects. These include most acidic foods, carbonated drinks, and spicy foods.
Urinary tract infection (UTI)

UTI can attack any part of the urinary tract.
Causes of UTI and its symptoms tend to vary with age. For instance, in children, UTI can be due to holding back urine or making it habit to hold it back . Additionally, this could be caused by the actual burning sensation.
Other causes or reasons why you get UTI include:
- Young females who do not wear (undergarment) or underwear
- Men with prostate disease
- Fungal infection
- TB in the urinary tract or system
UTI can affect both males and females but more common in females. This is attributed to their anatomy. The risk of getting UTI is higher at old age in females.
Urethritis

This is another cause of pain in urethra during urination.
Urethritis is the inflammation of the urethra due to many infectious or non-infectious conditions. There inflammation can occur in absence of infection symptoms. In fact, some people show/have not these symptoms.
- Difficulty to start urination
- Discomfort during intercourse
- Fever and chills
- Stomach pain, abdominal or pelvic pain
- Itching and (vaginal discharge in women or from the penis in men)
- Blood in urine (in men)
- Painful ejaculation
The lymph nodes may become swollen or get enlarged.
NOTE: As stated, urethritis can be due to an STI (such as gonorrhea) or be non-gonococcal (gonorrhea not a primary cause).
One of the infection risks for urethritis is when and after the infection causing virus or bacteria enters the body through the urethral opening.
Sexually transmitted infections (STIs)

Some of the sexually transmitted diseases (STIs) associated with painful urination include the following.
Bacterial or Gonococcal urethritis
More often, urethritis is caused by a bacteria. In many cases, gonorrhea and chlamydia are responsible for STI-related urethritis.
Like gonorrhea, chlamydia is also spread through direct sexual contact with an infected person. Namely, oral, vaginal or anal sex.)
IMPORTANT: Pregnant women can give their babies chlamydia at the point of delivery.
If you suspect you have gonorrhea it is highly recommended that you also get tests for chlamydia since these can co-occur.
Gonococcal arthritis
This form of arthritis affects the joints but may involve the skin. It is an infection caused by Gonorrhea Neisseria.
Symptoms of gonococcal arthritis
- Skin Rashes
- Fever
- Abdominal pain or joint pain especially the knee, wrist, and ankles
- Pain during peeing
- Pain in wrist due to inflammation of the tendons
After undergoing medical examination and tests, your doctor will determine the most suitable form of treatment.
According to medical information by the Medline Plus, the best way to control and prevent gonorrhea.
Urinary or urethral obstruction (Obstructive nephropathy)

Urinary obstruction is the result of impairment of the urinary flow along the urinary tract.
Some of the causes of urethral or urinary tract obstruction comprise problems within walls or in the walls or exertion of some kind of pressure from the surrounding body parts or a problem that leads increase in pressure such as pancreatitis or pelvic tumors.
Notably, one of the most common causes of obstruction in males is a consequence of urethral stricture. Urethral stricture is the narrowing of the urethra and may be caused by injury, infectious urethritis, and non-infectious urethritis.
This problem is more common young people and the old.
Urethral obstruction can be acute or chronic and may affect both (ureters) – tubes that allow for a flow of urine from the kidney.
Acute bilateral obstructive uropathy
According to the New York Times Health Guide, acute bilateral obstructive uropathy occurs when the obstruction comes suddenly.
This blockage causes urine not to flow from the kidneys (both) as it should.
Men and women equally can acute bilateral obstructive uropathy. The major cause of this is enlarged prostate in men. Additionally, bladder cancer, prostate cancer and kidney stones, blood clots, neurogenic bladder, papillary necrosis can also be the reasons for this.
Symptoms
People with acute bilateral obstructive uropathy, there is a burning sensation during urination. Other signs and symptoms include:
- Presence of blood in urine or abnormal color of urine
- Frequent urge to go to the pee
- A decrease in blood pressure
- Reduced urine volume/day
- Incomplete emptying the bladder due to weak urinary tract
Individuals have a fever and an urge to urinate at night. Sometimes there is a pain on both sides of the pelvic area.
For some or certain symptoms to be confirmed please, see a urologist or specialist at a clinic.
Non-gonococcal urethritis
If you are not sexually active and suspect you have urethritis, chances are likely that you may have the non-gonococcal urethritis.
Like bacterial or gonococcal urethritis, this form of inflammation of the urethral passage may show up almost with similar symptoms. Some people, men in particular sometimes have no signs such as discharge.
However, pin or the burning feeling while passing urine is evident in non-gonococcal urethritis.
In females, non-gonococcal urethritis almost always has no symptoms.
Genital herpes
Genital herpes or herpes simplex of the genital is an infection of the mucous membrane or skin caused by the herpes simplex virus (most often the HSV-2) virus.
The most common way through which HSV-2 spreads from the infected person to the other is by having sexual contact, the intercourse of making contact with the contagious sores.
Symptoms
Symptoms may vary in terms of appearance from the time infection occurs to the time the sores heal. These include:
- Painful fluid-filled blisters on the outer vagina lips, cervix in women
- Painful ulcers after the sores break to let out fluid
- Blisters on lips, fingers, the lips, and other oral parts
In both men and women, a painful urination sometimes with discharge may occur.
Treatment and remedies

Medicines prescribed by your physician help deal with symptoms such as pain due to the sores. These include antiviral medicines, painkillers and anti-itch medication.
Due to the fact that genital herpes cannot be cured, recurrence is likely. Although some people never have the noticeable symptoms, transmission can still happen.
Infected persons are there encouraged to reduce stress which can trigger the second episode of genital or kip herpes.
Pregnant women diagnosed of genital herpes can receive treatment in last one or so months if clinical recommendations allow.
Dehydration
Can dehydration or not drinking enough water lead to burning when urinating? Body dehydration is not marked by thirst hunger feeling or a dry mouth but would also be signified by the color, amount and “strength” of urine odor.
In females

This urination problem can affect females. In addition to the (general or reasons in particular as discussed), painful urination or one with a burning can be due to the following.
- Irritation of vaginal tissue. This may be due to trauma from sexual activity, bubble bath,, chemical irritants in perfumes or lotions
- Vulvovaginitis
- A sign or manifestation of any change of vaginal tissue especially in menopausal women
- Radiation therapy (as a treatment or therapy for cancer of internal tissue)
Grownup pregnant women are encouraged to have a regular visit to a clinic for evaluation. If you are sexually active, restrain from sex if you have been treated of any STIs recently.
In males
In addition to our discussion, the following are major causes for painful urination in males including risks.
- Gonococcal urethritis
- Non-gonococcal urethritis such as chlamydia and catheter replacement
- Penile trauma
- Kidney infection
Other causes

- Urinary tract neoplasm –
- Streptococcal Group B invasive disease
- Urosepsis (burning sensation during urination)
- Vulvovaginitis – burning during urination in females
- Pain due to external lesions on the penis or vaginal or labia sores
- Cystine stones
Painful sensation
A summary of common factors associated with painful urination or which cause pain while peeing include:
- Acute bacterial prostatitis
- Urinary catheter infection
- Acute bilateral obstructive uropathy
- Gonococcal urethritis
- Non-gonococcal urethritis
- Urinary tract neoplasm
Urination and cancer signs
According to the Prostate Cancer Foundation, early signs of prostate cancer may go unnoticed for many people. However, as the tumors containing cancer cells grow, they cause some form of blockage or urinary dysfunction.
The following could be signs that you may have a prostate cancer.
- Weak urinary stream hence inability to start or stop urination in case it starts (incontinence)
- Difficulty urinating when standing up
- Leaking or dribbling due to the feeling of “fullness in bladder”
- Pain or stiffness in the lower back including the hips, or upper thigh
- Increasing pain while urination or a burning feeling sensation
More importantly, these symptoms/signs do not confirm that you have prostate cancer. For instance, in men, some of these could be an indication of prostate enlargement.
Symptoms that may prompt a medical examination include painful ejaculation, the presence of blood in the urine or semen, erectile dysfunction and bone pain although they are rare in cases of prostate cancer signs.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis would include the following things (some may not be necessary but you may be asked to get certain tests.)
- Physical examination of the pelvis and the genital area for any abnormalities
- Laboratory tests for the discharges
- Urine tests
- Plain X-rays
Your doctor could also ask you about how you are feeling or the symptoms that you have.
Treatment or prevention
Burning while urinating or after treated differently according to the causes. While some treatments can only get rid of the symptoms, certain medications will help to ease off the discomfort.
To help prevent certain STIs or complications that may come with it avoid sexual contact until your primary care provider shows you a green light.
- Go for cancer screening
- Consult your healthcare provider before medications especially during pregnancy
- Always go with your partner(s) to have tests
- Make any follow-up on medication when you have been requested
- Adhere to medical advice on medication or post-treatment self-care by your doctor who treated you personally
When to seek medical attention

Warning symptoms which must prompt for an immediate medical attention include
- Abnormal urine color/odor’
- High fever
- Pelvic pain
- Joint pain, sores or lesions
- A severe headache
- Frequent urination
Frequent burning urination and pain or after releasing urine can be a severe source of discomfort but if you have certain symptoms such as the presence of blood in urine or semen always see a medic.
