Sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) are a significant public health concern worldwide. Many STDs, including chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HIV, can be asymptomatic, meaning individuals may not realize they are infected. This makes regular testing crucial for early detection and treatment.
Getting checked at an STD clinic ensures that infections are identified and managed before they lead to more severe health complications.
When Should You Get Tested?
The frequency of STD testing depends on several factors, including lifestyle, sexual activity, and medical history. Here are some key guidelines:
Before engaging in a new sexual relationship: It is advisable for both partners to get tested before becoming intimate.
If you experience symptoms: Signs such as unusual discharge, pain during urination, sores, or itching in the genital area warrant immediate testing.
Annually for sexually active individuals: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends yearly screenings for sexually active individuals, especially those under 25 or with multiple partners.
More frequently for high-risk groups: Those with multiple partners, a history of STDs, or who engage in unprotected sex should get tested every 3 to 6 months.
Pregnant women: Routine STD testing is advised during pregnancy to prevent complications for both the mother and baby.
Why Regular Testing Is Essential
Early Detection and Treatment
Many STDs are manageable with early diagnosis and treatment. If left untreated, infections can lead to complications such as infertility, pelvic inflammatory disease, and an increased risk of contracting HIV. Regular testing allows for timely intervention and better health outcomes.
Protecting Your Partner’s Health
Since STDs can be transmitted even when symptoms are not present, regular screening helps prevent unknowingly spreading infections to partners. This ensures that both you and your partner remain safe and healthy.
Reducing Stigma and Normalizing Testing
Many people hesitate to visit an STD clinic due to fear or embarrassment. However, normalizing STD testing as part of routine healthcare encourages responsible sexual health practices. By openly discussing and prioritizing testing, individuals can contribute to reducing stigma and making sexual health a regular conversation.
Avoiding Long-Term Health Risks
Some STDs, like HPV and herpes, have long-term effects if left untreated. HPV, for example, is linked to cervical cancer, while untreated syphilis can lead to neurological damage. Routine testing minimizes the risk of severe health conditions and ensures prompt medical attention.
What to Expect During an STD Test?
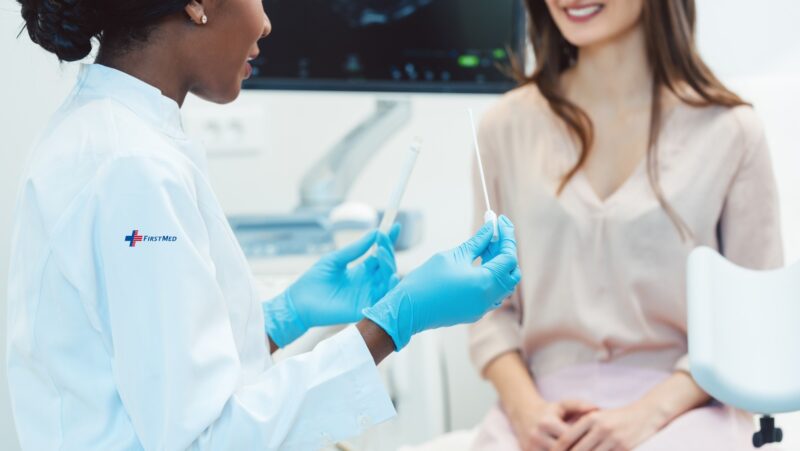
STD testing varies depending on the type of infection being checked. Common tests include:
Urine tests: Used to detect chlamydia and gonorrhea.
Blood tests: Essential for diagnosing HIV, syphilis, and hepatitis.
Swab tests: Taken from the throat, rectum, or genital area to detect bacterial infections.
Physical examinations: Some STDs, like genital warts, may require a visual inspection by a healthcare professional.
The testing process is typically quick, confidential, and painless. Results may be available within a few days, allowing individuals to receive treatment if necessary.
How to Find an STD Clinic?
If you are unsure where to get tested, local healthcare providers, community health centers, and dedicated STD clinics offer confidential and professional testing services. Many clinics also provide free or low-cost testing options to ensure accessibility for all individuals.
Conclusion
Regular STD testing is a crucial aspect of maintaining sexual health. By getting tested regularly, individuals can protect their health, prevent the spread of infections, and reduce the stigma surrounding STD screening. Whether you have symptoms or not, visiting an STD clinic for routine check-ups ensures peace of mind and long-term well-being. Prioritizing sexual health is not just about personal well-being but also about safeguarding the health of partners and the broader community.

