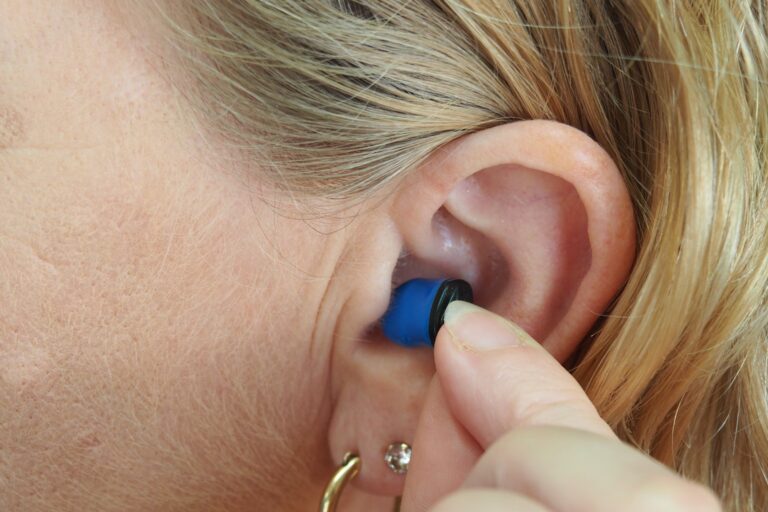
Hearing loss is common among people aged 12 years and above. According to a recent study, over 1.5 billion people worldwide suffer from hearing loss. When left untreated, hearing loss results in increased cognitive decline, social isolation, and depression. An effective way to correct hearing loss and improve your quality of life is by investing in hearing aids. Here is everything you need to know about hearing aids.
What are hearing aids?
Hearing aids are small electronic devices worn behind or inside your ears. They make sounds louder, enabling persons with hearing loss to listen and communicate efficiently. A digital hearing aid has a microphone that picks up sound, a computer chip that processes and amplifies the sound, and a speaker that conveys the signal to your ears. Hearing aids also have batteries for power.
When do you need hearing aids?
If you are constantly watching people’s lips during a conversation instead of making eye contact, continually saying “pardon” or “repeat,” or having difficulties following discussions, it could signify you have a degree of hearing loss. However, this does not mean you should go ahead and purchase hearing aids.
If you suspect you have trouble hearing, consider scheduling a hearing test with a reputable audiologist. An audiologist can determine whether or not you have hearing loss. They can also establish whether an amplification will be beneficial.
A hearing test can also help you determine whether other issues, such as injuries, wax build-up, and infections, could be causing hearing loss. Visit HearCanada to schedule a hearing test to determine whether you need to invest in hearing aids.
How hearing aids help with hearing
Audiologists often recommend hearing aids to people with a type of hearing loss called sensorineural. Sensorineural hearing loss is caused by damage to the small sensory cells in your inner ear. This damage results from aging, injury from certain medications and noise, or diseases.
Hearing aids amplify the sound vibrations entering the ears. The surviving hair cells then pick up these sounds and transmit them to the brain as neural signals through the auditory nerve. The more damaged your inner ears are, the greater the hearing loss severity, necessitating greater hearing aid amplification. A hearing aid cannot convert even the largest vibrations into neural signals if your hair cells are too damaged. In this case, the hearing aid will be ineffective.
Types of hearing aids
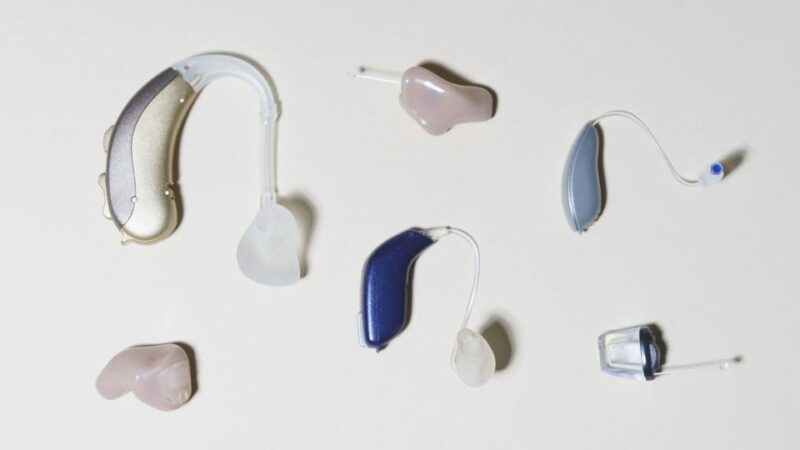

Hearing aids function differently based on the electronics used. Here are the two main types of hearing aids.
1. Digital hearing aids
Before amplifying, digital hearing aids change sound waves into numerical codes. The numerical codes often include information about the loudness and pitch of the sound. This means that these hearing aids can be programmed to focus on sounds coming from certain directions and amplify specific frequencies. Digital aids can also be adjusted to focus on sounds from a particular direction. This enables your audiologist to tailor your hearing aids to your needs and the specific listening environments.
2. Analog hearing aids
These hearing aids change sound waves into electrical signals before amplifying them. Analog hearing aids are customized to suit each user’s different needs. Analog hearing aid manufacturers often develop these devices according to your audiologist’s specifications.
Analog aids entail more than one setting or program, and your ear doctor can program them using a computer. Whether in a crowded, quiet, or small room, you could also change your analog aids settings to suit the environment. This hearing aid type is also less expensive than digital aids. The analog circuitry is also suitable for all hearing aid types.
The different styles of hearing aids

Hearing aids differ significantly in size, price, and placement in your ears. Below are the typical hearing aid styles.
1. In the ear hearing aid
In-the-ear (ITE) hearing aids are designed to fit entirely inside the outer ear. They feature a hard plastic casing that houses the electronic components. ITE aids are suitable for persons with severe to mild hearing loss.
Some in-the-ear hearing aids contain additional features such as a telecoil. Telecoils are small magnetic coils that enable you to receive sound waves via the hearing aid circuitry instead of the microphone. This makes hearing a conversation over a mobile phone easier.
ITEs also contain features like volume control that only fits smaller hearing devices. They are also more visible, easier to handle, and use larger batteries, increasing their battery life. However, ITEs are also vulnerable to earwax buildup and clogging. They may also not be suitable for small children because you must keep replacing the casing as your baby’s ears grow.
2. Behind-the-ear hearing aid
A behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aid features a hard plastic case that sits behind your ear. It also has a plastic ear mold that fits inside your outer ear and conveys sound waves to your ear. This hearing aid style is suitable for people of all ages and can be used to correct mild to severe hearing loss.
There is also a new type of BTE hearing aid: the Mini BTE that fits behind the ear completely. It has a narrow tube inserted inside the ear canal, allowing it to stay open. The narrow line also prevents earwax build-up and enables you to hear your voice.
3. Canal hearing aid
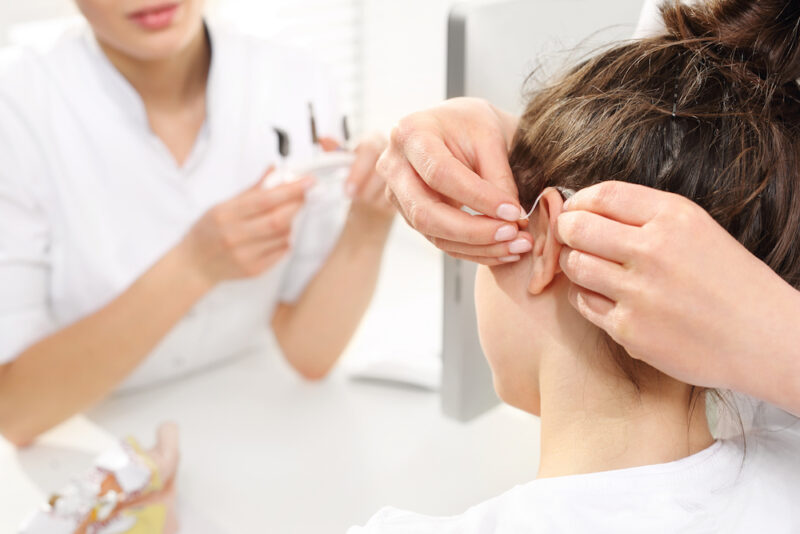
A canal hearing aid is inserted into the ear and is less visible. There are two styles of canal hearing aids: Completely-in-Canal (CIC) and In-the-Canal (ITC). A completely-in-canal hearing aid is a smaller device and is nearly hidden inside the ear. ITC aids are designed to fit the shape and size of your ear canals.
Canal hearing aids can correct moderately severe to mild hearing loss. However, thanks to their small size, canal hearing aids may not be suitable for children or adults with issues with tiny devices.
Endnote
Hearing aids are small electronic devices that make sounds louder, enabling you to jump back into your social life. Familiarize yourself with the different hearing aids styles and types, how they help with hearing, and when you need them. However, ensure you schedule a hearing test before investing in hearing aids to determine the severity of your hearing loss and the best hearing aid type and style for you.