Whether it’s for a routine check-up or to investigate an issue, medical imaging like CT scans and MRIs are essential tools in modern healthcare. These scans help doctors see inside your body without surgery, providing critical information to diagnose and treat various conditions. But what exactly are these scans, and how do they differ?
Let’s explore the science behind CT scans and MRIs and understand their real differences. For more detailed info, you can check out https://easymedical.co.il/en/.
How a CT Scan Works
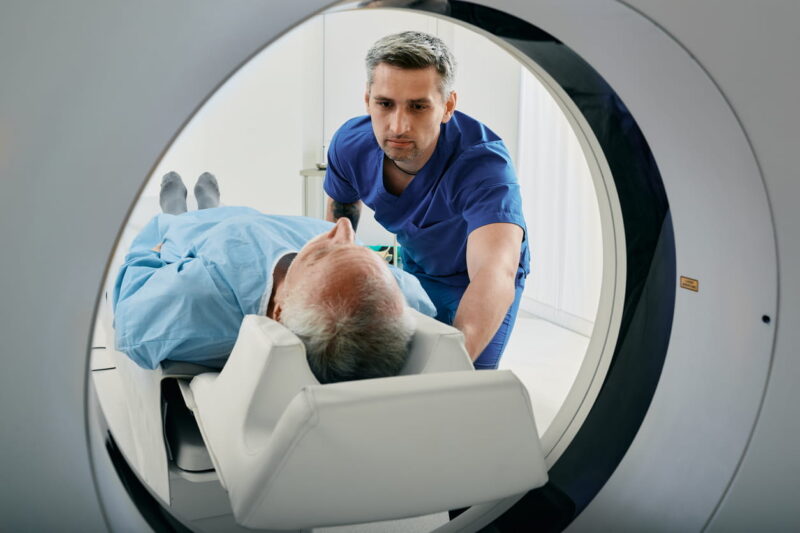
A CT (Computed Tomography) scan combines X-ray images taken from different angles around your body and uses computer processing to create cross-sectional images (slices) of the bones, blood vessels, and soft tissues inside your body. Think of it as looking at a loaf of bread one slice at a time, but in much greater detail.
During a CT scan, you lie on a motorized table that moves through a circular opening of the scanner. The X-ray tube rotates around you, capturing multiple images. These images are then sent to a computer, which constructs detailed 3D images. The whole process is quick and usually takes about 10-30 minutes.
When is It Used?
CT scans are particularly useful for:
- Detecting bone fractures
- Diagnosing lung and chest problems
- Spotting cancers
- Guiding certain treatments, such as surgery or radiation therapy
- Detecting internal bleeding and injuries
What is an MRI?
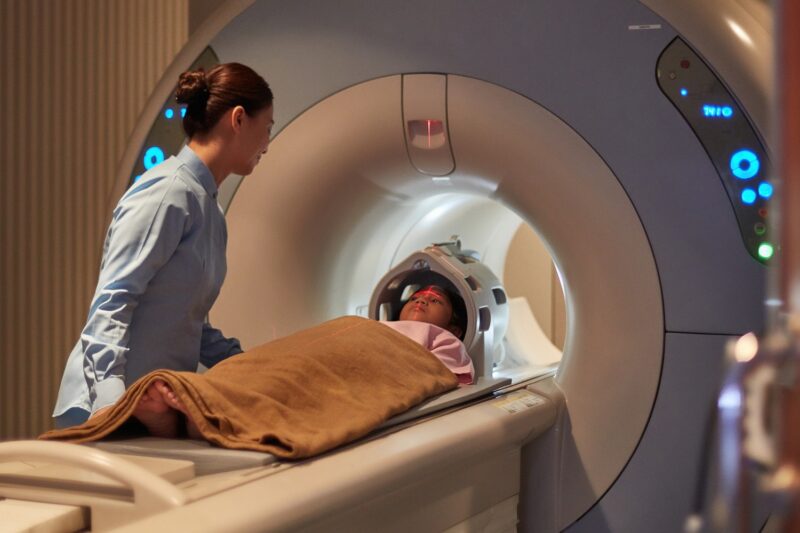
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate detailed images of the organs and tissues within your body. Unlike CT scans, MRIs do not use ionizing radiation, making them a safer alternative for frequent imaging.
During an MRI, you lie on a table that slides into a long, narrow tube. The machine’s magnetic field temporarily realigns hydrogen atoms in your body. Radio waves then cause these atoms to produce faint signals, which are used to create cross-sectional MRI images. This process can take longer than a CT scan, usually between 30-60 minutes.
When is ItI Used?
MRIs are ideal for:
- Examining the brain and spinal cord
- Diagnosing torn ligaments and other soft tissue injuries
- Detecting tumors in soft tissues
- Evaluating joint abnormalities
- Monitoring certain chronic conditions, such as multiple sclerosis
Key Differences Between CT Scans and MRIs
Understanding the key differences between CT scans and MRIs can help you know when and why each imaging method is used:
Imaging Technique
- CT Scans: Use X-rays to produce images.
- MRIs: Use magnetic fields and radio waves.
Radiation Exposure
- CT Scans: Involve exposure to ionizing radiation.
- MRIs: Do not use ionizing radiation.
Detail and Clarity
- CT Scans: Better for imaging bones and detecting acute injuries and lung issues.
- MRIs: Provide superior detail for soft tissues, such as the brain, muscles, and ligaments.
Time and Comfort
- CT Scans: Typically quicker, taking about 10-30 minutes.
- MRIs: Longer, taking about 30-60 minutes, and can be uncomfortable for those who are claustrophobic.
Safety Considerations
CT scans involve exposure to ionizing radiation, which can increase the risk of cancer over time. However, the risk is generally low and is often outweighed by the benefits of accurate diagnosis and treatment.
MRIs do not use ionizing radiation, making them safer for repeated use. However, they are not suitable for people with certain implants, such as pacemakers or cochlear implants, due to the strong magnetic field.
Choosing Between a CT Scan and an MRI
When choosing between the two methodsm consider the following factors:
- Type of Condition: For bone fractures or lung issues, a CT scan is usually preferred. For soft tissue evaluation, an MRI is better.
- Urgency: CT scans are faster, making them suitable for emergency situations.
- Patient’s Medical History: Patients with implants or those who need frequent imaging may benefit more from MRIs due to the lack of radiation exposure.
Consult Your Doctor
Your doctor will consider these factors and more when deciding which imaging method is best for you. Always discuss any concerns or preferences you have with your healthcare provider.
The Bottom Line
CT scans and MRIs are both incredible tools in modern medicine, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding how they work and their differences can help demystify the process and alleviate any concerns you might have.

