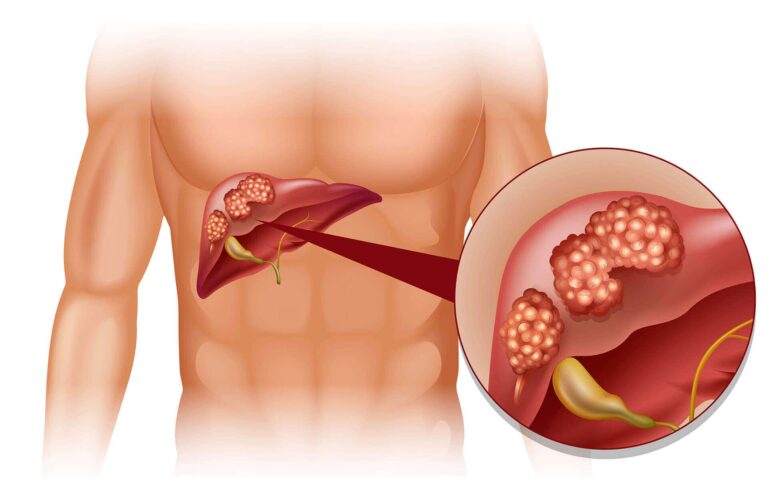
In its simplest form, liver cancer refers to a type of cancer that appears in the cellules of the liver. It is an organ positioned in the upper right area of the abdomen. Many vital functions are carried out by it, such as screening the blood, storing energy, and making enzymes and bile for digestion.
However, there is good news. This is one of the most treatable cancers if it is caught early. With new advances in treatment, the survival rate for liver cancer has increased dramatically in recent years. In this article, let’s take a look at its causes, signs, risk factors, and therapy options. Keep reading to gain more information which will help you to better understand this disease.
Types Of Primary Liver Cancer
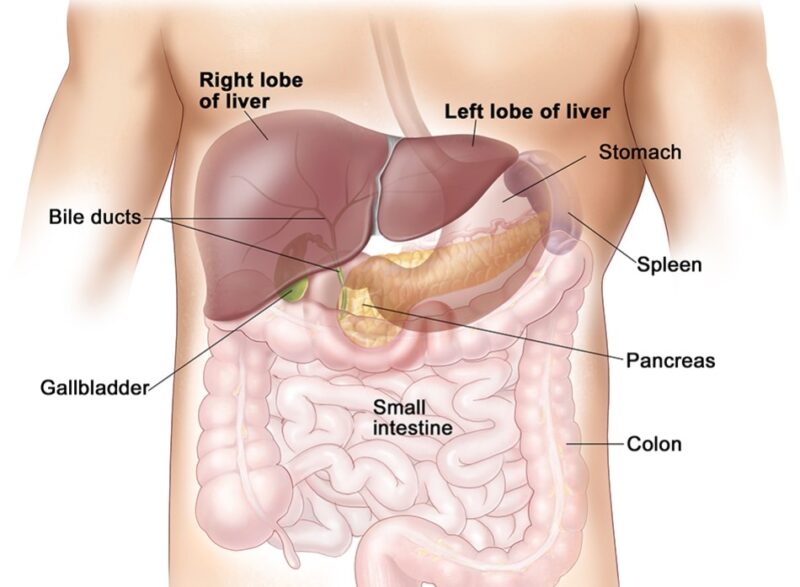
There are three leading forms of primary liver cancer: angiosarcoma, intrahepatic (within the hepatic tissue), and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC).
- Angiosarcoma typically starts as a small lump on one side of the organ. Over time, this lump may grow larger until it becomes an invasive tumor. It sprawls to other body parts (inclusive of lymph nodes) and can be noxious if not treated quickly.
- Intrahepatic cancer (IHC) accounts for about 25% of all cases. IHC occurs when abnormal cells from elsewhere in the body invade and grow in the hepatocytes.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) arises from malignant transformation within hepatocytes rather than invasion by external agents.
Since it is a deadly disease, it is wise to act fast. So, getting help from a HIPAA-compliant liver cancer community is crucial if you have been diagnosed with primary liver cancer. Many resources are accessible to help you endure your diagnosis and treatment. The most crucial thing is getting the regimen started as soon as possible.
Causes
There are many different reasons for this disease. While you might not know everything about this disease, researchers have been able to identify some of the most common causes, which are outlined below:
1)Long-term inflammation: Liver cells mutate in their DNA due to long-term inflammation. This can happen because of things like chronic hepatitis infections, chemical process exposure, or even obesity.
2) Liver cell mutation: Certain liver cells are more likely to mutate and develop into tumors. This may be due to long-term exposure to chemicals or radiation or the result of your genes.
3) Tumor formation: If these mutations and exposures occur over time, they will ultimately form a tumor. Masses of cancerous cells will grow together until they’re large enough to cause harm to liver function.
4) Chronic hepatitis infection: It can detriment your liver over time, allowing other factors (like alcohol abuse or viral hepatitis B) to contribute to further damage.
Risk Factors Associated With Liver Cancer

The points below outline some of the most common risk factors for this disease. Knowing about these risks can help you take steps to lower your chances of developing the disease.
- Alcohol abuse: Heavy drinking increases the risk of this disease.
- Obesity and hepatitis infection: People who are obese or have hepatitis B or C virus preside to develop the disease.
- Smoking: Cigarette smoking is the leading cause of the disease worldwide.
- Hemochromatosis: This condition occurs when your body accumulates too much iron.
- Cirrhosis: It occurs when the usual protective barriers that protect from toxins and harmful chemicals are damaged or destroyed.
- Diabetes: It proliferates your risk of advancing cirrhosis and liver cancer.
- Nonalcoholic fatty disease: It is a condition in which excess fat builds up inside your hepatocytes, leading to inflammation and damage to the organ.
- Having foods with aflatoxin: A severe complication after eating contaminated food.
Symptoms
It is very important to know the symptoms and get checked out by a doctor if you notice any of them. Here are some common symptoms of the disease:
- Abdominal pain or swelling may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
- Itching or a rash on the skin that does not go away when treated with topical medications.
- Jaundice due to an increase in bilirubin levels.
- Fatigue.
- Dark urine.
- Fever.
- Weight loss.
- Loss of appetite.
The Different Stages Of Liver Cancer
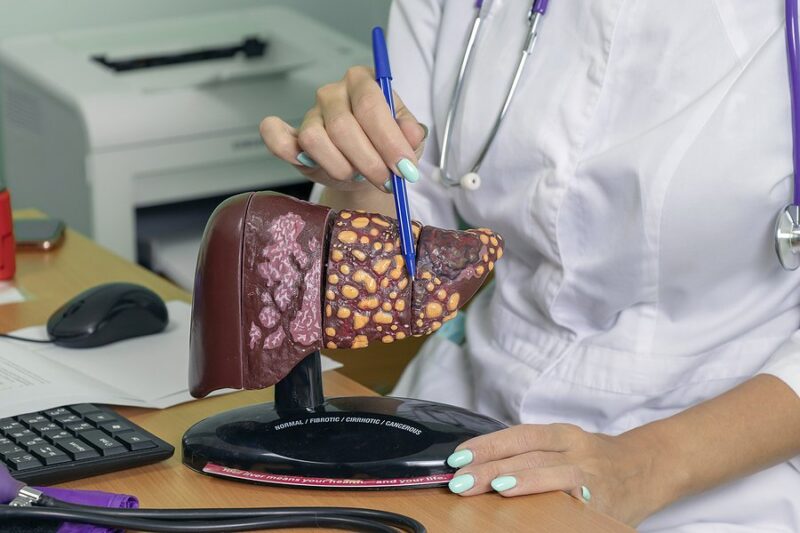
The disease progresses through four stages, and each stage has its own set of symptoms. If you or someone you know is experiencing some of these symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention right away.
- Stage 1: It is characterized by a single tumor beneath 2 centimeters in size.
- Stage 2: It is similar to Stage I, but the tumor is more prominent, measuring 5 centimeters or less. In addition, Stage II may build out to nearby blood vessels.
- Stage 3: This stage occurs when multiple tumors are present, one more significant than five centimeters. This stage may also involve the transmission of cancer to other organs or lymph nodes.
- Stage 4: This is the peak progressive phase of the disease where cancer can build out to other body parts, particularly the bones or lungs, and may actually be prevailing in lymph nodes.
Diagnosis
There are different types of diagnosis to detect the disease: Blood test, Ultrasound, CT scan, MRI, Angiogram, and Surgical biopsy.
- Blood tests can help to identify abnormal levels of certain substances produced by the liver, such as bilirubin and tumor markers.
- An ultrasound (sonography) uses sound waves to actualize an image of the liver and can help to ascertain a mass or tumor.
- A computed tomography scan also effectuates images of the body but uses X-rays rather than sound waves. This scan can help conclude if a mass is solid or filled with fluid.
- Magnetic resonance imaging involves magnetic fields and radio waves to effectuate comprehensive images of organs and tissues in the body, which can help determine small tumors.
- Another such test is an angiogram. This test involves dye and distinctive x-ray equipment to take pictures of the blood vessels in your liver. The results of this test will help your doctor to adjudicate if surgery is an option for you.
- The biopsy procedure help to remove a small segment of tissue from the liver so it can be inspected under a microscope for signs of cancer.
After all test results have been reviewed, your doctor will stage your cancer. This helps determine how aggressive your treatment will need to be and what your prognosis (outlook) may be.
Treatment Options Available For Liver Cancer

There are a number of treatment options available for this disease. The type of treatment you receive will depend on the stage of the cancer, your overall health.
- Surgery: The surgery typically involves removing part or all of the tumor using open or laparoscopic surgery. Depending on the size and location of the tumor, other procedures may also be performed (for example, ablation).
- Embolization: It is a procedure that uses small embolic particles (usually made from materials like latex) to block blood flow to tumors.
- Ablation: It is a surgical technique that uses high-intensity heat to destroy tumors.
- Chemotherapy: It is an arrangement of drugs that are carried out intravenously or orally over several weeks or months.
- Radiation therapy: It includes high-energy rays to damage the tumor and kills any cancer cells that have spread.
- Immunotherapy: It uses the body’sbody’s natural defenses to fight cancer. This treatment targets specific proteins in the tumors that help them grow and survive.
Conclusion
If you’re reading this, it’s likely because you or someone you know has been diagnosed with liver cancer. You can do many things to help lower your possibility of developing the disease. Try to establish a healthy weight and avoid excessive drinking and smoking.
Take medical attention immediately if you have liver cancer or notice any changes in your body or unexplained pain. Early detection is critical in treating liver cancer.